힙(heap)
- 최댓값과 최솟값을 빠르게 찾기 위해 고안된 자료구조
- 완전 이진트리
- 힙 property
- A가 B의 부모노드이면 A의 키값과 B의 키값 사이에는 대소 관계가 성립한다.
최소 힙
- 부모 노드의 키값이 자식 노드의 키값보다 항상 작은 힙
최대 힙
- 부모 노드의 키값이 자식 노드의 키값보다 항상 큰 힙
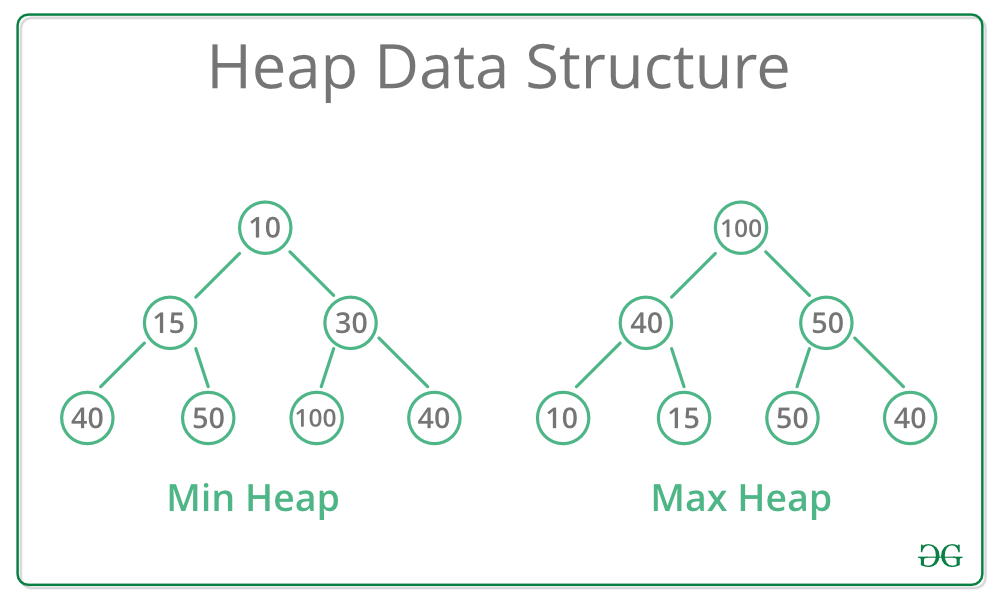
- 힙에서는 가장 낮은(혹은 높은) 우선순위를 가지는 노드가 항상 루트에 오게 된다.
- 이를 이용해 우선순위 큐와 같은 추상적 자료형을 구현할 수 있다.
- 키 값의 대소 관계
- 부모/자식 노드 ⭕
- 형제노드 ❌
- 시간복잡도
- O(log n)
최소힙(heapq 모듈을 사용하지 않고 구현)
# 최소힙
# 힙 삽입 연산
def heap_push(item):
heap.append(item)
child = len(heap) - 1
parent = child // 2
# 루트 노드이거나 최소힙 조건을 만족하지 못하면 종료
while parent > 0 and heap[parent] > heap[child]:
heap[parent], heap[child] = heap[child], heap[parent]
child = parent
parent = child // 2
# 힙 삭제 연산
def heap_pop():
# 루트 노드만 남은 경우 바로 반환
if len(heap) <= 2:
return heap.pop()
item = heap[1] # 루트 노드 백업
heap[1] = heap.pop() # 마지막 노드를 루트 노드로 이동
parent = 1
child = parent * 2
while child < len(heap): # 자식이 하나라도 있으면
if child + 1 < len(heap) and heap[child] > heap[child + 1]:
# 오른쪽 자식이 있고, 오른쪽 자식이 왼쪽 자식보다 작다면
child += 1 # 비교 대상을 오른쪽 자식으로 갱신
# 자식이 더 작으면 최소힙이 아니므로 노드 교환
if heap[parent] > heap[child]:
heap[parent], heap[child] = heap[child], heap[parent]
parent = child
child = parent * 2
# 최소힙 만족하면 탈출
else:
break
return item # 백업했던 루트 노드 반환
heap = [0]
heap_push(2)
heap_push(5)
heap_push(7)
heap_push(3)
heap_push(4)
heap_push(6)
print(heap)
while len(heap) >= 2:
print(heap_pop())
최대힙(heapq 모듈을 사용하지 않고 구현)
# 최대힙
# 힙 삽입 연산
def heap_push(item):
heap.append(item)
child = len(heap) - 1
parent = child // 2
# 루트 노드이거나 최대힙 조건을 만족하지 못하면 종료
while parent > 0 and heap[parent] < heap[child]:
heap[parent], heap[child] = heap[child], heap[parent]
child = parent
parent = child // 2
# 힙 삭제 연산
def heap_pop():
# 루트 노드만 남은 경우 바로 반환
if len(heap) <= 2:
return heap.pop()
item = heap[1] # 루트 노드 백업
heap[1] = heap.pop() # 마지막 노드를 루트 노드로 이동
parent = 1
child = parent * 2
while child < len(heap): # 자식이 하나라도 있으면
if child + 1 < len(heap) and heap[child] < heap[child + 1]:
# 오른쪽 자식이 있고, 오른쪽 자식이 왼쪽 자식보다 크다면
child += 1 # 비교 대상을 오른쪽 자식으로 갱신
# 자식이 더 크면 최대힙이 아니므로 노드 교환
if heap[parent] < heap[child]:
heap[parent], heap[child] = heap[child], heap[parent]
parent = child
child = parent * 2
# 최대힙 만족하면 탈출
else:
break
return item # 백업했던 루트 노드 반환
heap = [0]
heap_push(2)
heap_push(5)
heap_push(7)
heap_push(3)
heap_push(4)
heap_push(6)
print(heap)
while len(heap) >= 2:
print(heap_pop())
힙큐(heapq)
- 파이썬 heapq 모듈은 heapq 알고리즘을 제공한다.
- 이진 트리 기반의 최소 힙(min heap) 자료구조를 제공한다.
- min heap을 사용하면 원소들이 항상 정렬된 상태로 추가되고 삭제된다.
- min heap에서 가장 작은 값은 언제나 인덱스 0 즉, 이진 트리의 루트에 위치한다.
- 내부적으로 min heap 내의 모든 원소(k)는 항상 자식 원소들 (2k+1, 2k+2)보다 크기가 작거나 같도록 원소가 추가되고 삭제된다.
heap[k] <= heap[2*k+1] and heap[k] <= heap[2*k+2]
1 ---> root
/ \\
3 5
/ \\ /
4 8 7
heapq 모듈을 이용한 최소힙
from heapq import heappush, heappop
heap = []
heappush(heap, 2)
heappush(heap, 5)
heappush(heap, 7)
heappush(heap, 3)
heappush(heap, 4)
heappush(heap, 6)
print(heap)
while heap:
print(heappop(heap))
- heapq 모듈은 파이썬의 보통 리스트를 마치 최소 힙처럼 다룰 수 있도록 도와준다.
- 파이썬에서는 heapq 모듈을 통해서 원소를 추가하거나 삭제한 리스트가 그냥 최소 힙이라는 것!
heapq 모듈을 이용한 최대 힙
from heapq import heappush, heappop
nums = [4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5]
heap = []
for num in nums:
heappush(heap, (-num, num)) # (우선 순위, 값)
while heap:
print(heappop(heap)[1]) # index 1
8
7
5
4
3
1
힙에 원소 추가
heappush()
from heapq import heappush
heappush(heap, 4)
heappush(heap, 1)
heappush(heap, 7)
heappush(heap, 3)
print(heap)
[1, 3, 7, 4]
- 가장 작은 1 이 인덱스 0에 위치한다.
- 인덱스 1(=k)에 위치한 3 은 인덱스 3(=2k+1)에 위치한 4 보다 크므로 힙의 공식을 만족한다.
힙에서 원소 삭제
heappop()
from heapq import heappop
print(heappop(heap))
print(heap)
1
[3, 4, 7]
- 가장 작았던 1 이 삭제되어 리턴되었고, 그 다음으로 작았던 3 이 인덱스 0이 되었다.
최소값 삭제하지 않고 얻기
- 리스트의 첫번째 원소에 접근하듯이 인덱스를 통해서 접근하면 된다!
# [3, 4, 7]
print(heap[0]) # 3
⚠️ 주의사항
- 힙(Heap)은 완전 이진 트리의 일종으로, 특별한 순서를 유지하는 배열이다.
- 힙은 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 작은 값을 갖도록 구성된 완전 이진 트리이다. 그러나 트리의 레벨별로 순서가 보장되어 있는 것은 아니다!
- 인덱스 0에 가장 작은 원소가 있다고 해서 인덱스 1에 두 번째로 작은 원소, 인덱스 2에 세 번째로 작은 원소가 있다는 보장은 없다!
- 힙은 heappop() 함수를 호출하여 원소를 삭제할 때마다 이진 트리의 재배치를 통해 매번 새로운 최솟값을 인덱스 0에 위치시킨다.
- 따라서 두 번쨰로 작은 원소를 얻으려면 heap[1] 으로 접근하면 안되고, 반드시 heappop() 을 통해 가장 작은 원소를 삭제 후에 heap[0] 을 통해 새로운 최솟값에 접근해야한다.
기존 리스트를 힙으로 변환
heapify()
from heapq import heapify
heap = [4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5]
heapify(heap)
print(heap)
[1, 3, 5, 4, 8, 7]
- heapify() 는 새로운 리스트를 반환하는 것이 아니라 인자로 넘긴 리스트에 직접 변경한다.
- 따라서 원본 리스트의 형태를 보존해야하는 경우에는 반드시 해당 리스트를 복제한 후에 인자로 넘겨야 한다!
nums = [4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5]
heap = nums[:]
heapify(heap)
print(nums)
print(heap)
[4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5]
[1, 3, 5, 4, 8, 7]
응용
n번째 최솟값/최댓값
nsmallest()
- 주어진 리스트에서 가장 작은 n 개의 값을 담은 리스트를 반환한다.
- 반환된 리스트의 마지막 값이 n 번째 작은 값이 된다.
from heapq import nsmallest
nsmallest(3, [4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5])[-1]
nlargest()
- n 번재 최댓값을 구한다.
from heapq import nlargest
nlargest(3, [4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5])[-1]
힙 정렬
from heapq import heappush, heappop
def heap_sort(nums):
heap = []
for num in nums:
heappush(heap, num)
sorted_nums = []
while heap:
sorted_nums.append(heappop(heap))
return sorted_nums
print(heap_sort([4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5]))
[1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8]
참고자료
https://www.daleseo.com/python-heapq/
파이썬의 heapq 모듈로 힙 자료구조 사용하기
Engineering Blog by Dale Seo
www.daleseo.com
'🛠️Language > python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [python] list 삭제 메서드 차이 + 요소 추가 (0) | 2023.06.30 |
|---|---|
| [python] 데크(deque)란? (0) | 2023.06.29 |